| Professor YAMAMOTO, Hideki |
- Development of automatic analysis system for flow characteristics of whole blood by small viscometer
- The HSP value is used for evaluation of solubility of polymers and pharmaceuticals, and evaluation of swelling behavior of rubbers and resins.
- The development of processes removing organic pollutants in wastewater by combining O3, UV and TiO2
- Development of new distillation regeneration process using salt effect on gas-liquid equilibrium of waste acid-water system
- The application of the saparation materials using self-response for external environment change of environment-responsive polymer gels
| Associate Professor ARAKI, Sadao |
- Development of Inorganic membranes for gas separation and liquid separation
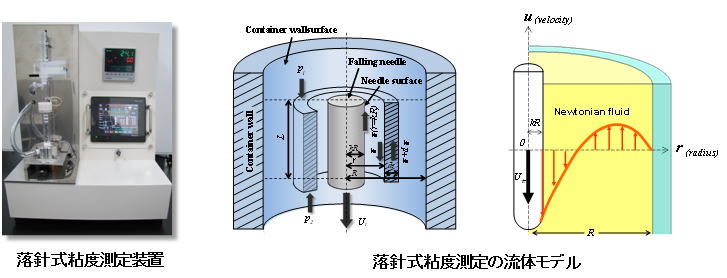
Development of automatic analysis system for flow characteristics of whole blood by small viscometer
Blood viscosity is an important basic physical property from the viewpoint of prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
However, from the problems of blood collection amount, measurement time, etc., it is not easy to measure the viscosity of blood immediately after blood sampling, and there are few cases of actual measurement.
In our laboratory, we have been developing a compact-size falling needle rheometer (FNR) that can measure the viscosity of blood with high accuracy, and in order to achieve high precision measurement and further improve operability, we are developing a new device incorporating automated analysis of blood viscosity measurement operation and automatic analysis system of flow characteristics.
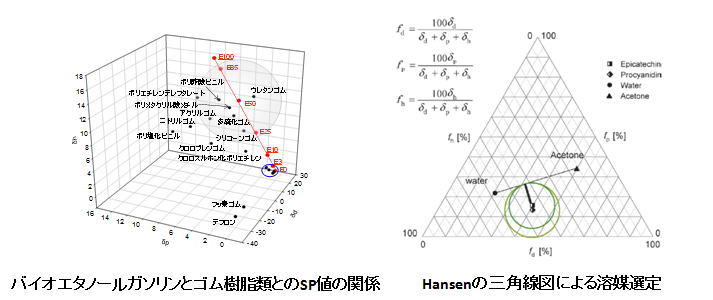
The HSP value is used as an index for evaluating the affinity between substances
The HSP value is used for evaluation of solubility of polymers and pharmaceuticals, and evaluation of swelling behavior of rubbers and resins.
This laboratory applies HSP values to various fields such as fine particles ionic liquids and surfactants. Affinity evaluation using HSP value is thought to be not only a tool for developing new materials, but also leads to faster research and development and lower cost.
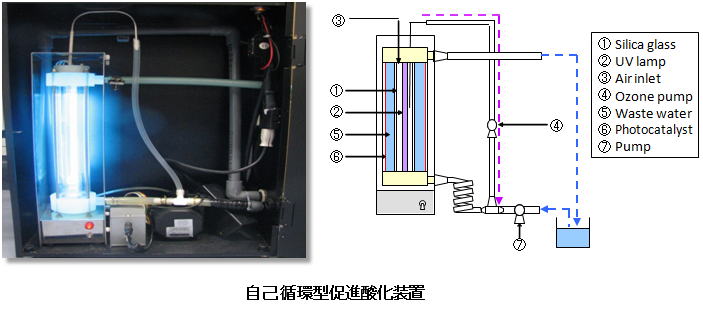
The development of processes removing organic pollutants in wastewater by combining O3, UV and TiO2
Many toxicity and persistent decomposable organic materials may be contained in wastewater generated from chemical plants, and if released as it is, it will remain in the natural environment for a long time to cause environmental pollution. Recently, it is not possible to deal with conventional water treatment technology such as biological treatment and adsorption treatment with activated carbon in some cases. As more advanced water treatment technology, Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) which combine with treatment such as UV light, ozone and photodecomposition by photocatalyst are paid attention.
In this laboratory, that’s aiming for oxidation decomposition of toxicity organic pollutants in wastewater by AOPs combined with UV, ozone and semiconductor photocatalyst. Furthermore we don’t use large set spaces and a ozone generator having problems such as high running cost, and we build the experiment equipment of self-circulation type of ozone which can generate ozone in the equipment. As the result, the characteristics in this equipment researched the performance can treat wastewater for an unnecessary ozone generator, space-saving design, energy conservation and lower cost by irradiating oxygen in air with UV and generating ozone.
Development of new distillation regeneration process using salt effect on gas-liquid equilibrium of waste acid-water system
In the semiconductor manufacturing process, mixtures of hydrofruoric acid, nitric acid and other acids are often used as washing or etching solutions for silicon wafers.
In this laboratory, the salt effect on vapor-liquid equilibrium of nitric acid-water systems was measured, and a distillation method for separation of nitric acid from acid mixture was been presented. This study presents the distillation treatment of hydrofluoric acid with use of the salt effect on the vapor-liquid equilibrium for acid aqueous solutions and acid mixtures. As a salt to be added, cesium nitrate, potassium nitrate and potassium fluoride are selected and the salt effect on the vapor-liquid equilibrium relationship of nitric acid-water system and hydrofluoric acid-water system is measured and a separation process is proposed.
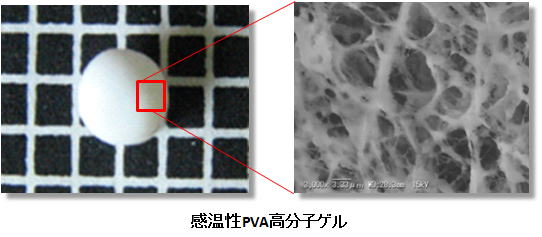
The application of the separation materials using self-response for external environment change to environment-responsive polymer gels
Some polymer gels have unique substance forms in which solids and liquids coexist, so they respond by sensing various physical and chemical information (temperature, solvent composition, pH, electric field, light etc.) in the external environment.
These gels are called environment-responsive polymer gels, and the applications are expected. Particularly, polymer gels that change physical properties and shape changes are called temperature-sensitive polymer gels or heat-sensitive polymer gels, and they have been researched the application of artificial muscle and drug delivery systems.
In this laboratory, we synthesize a polymer gel containing polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as a main component. We evaluate the physical properties of synthesized PVA polymer gel and adsorbent for trace organic materials.